Xu et al published a paper titled "Near-Infrared CMOS Image Sensors Enabled by Colloidal Quantum Dot-Silicon Heterojunction" in MDPI Electronics.
Link: https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9292/12/12/2695
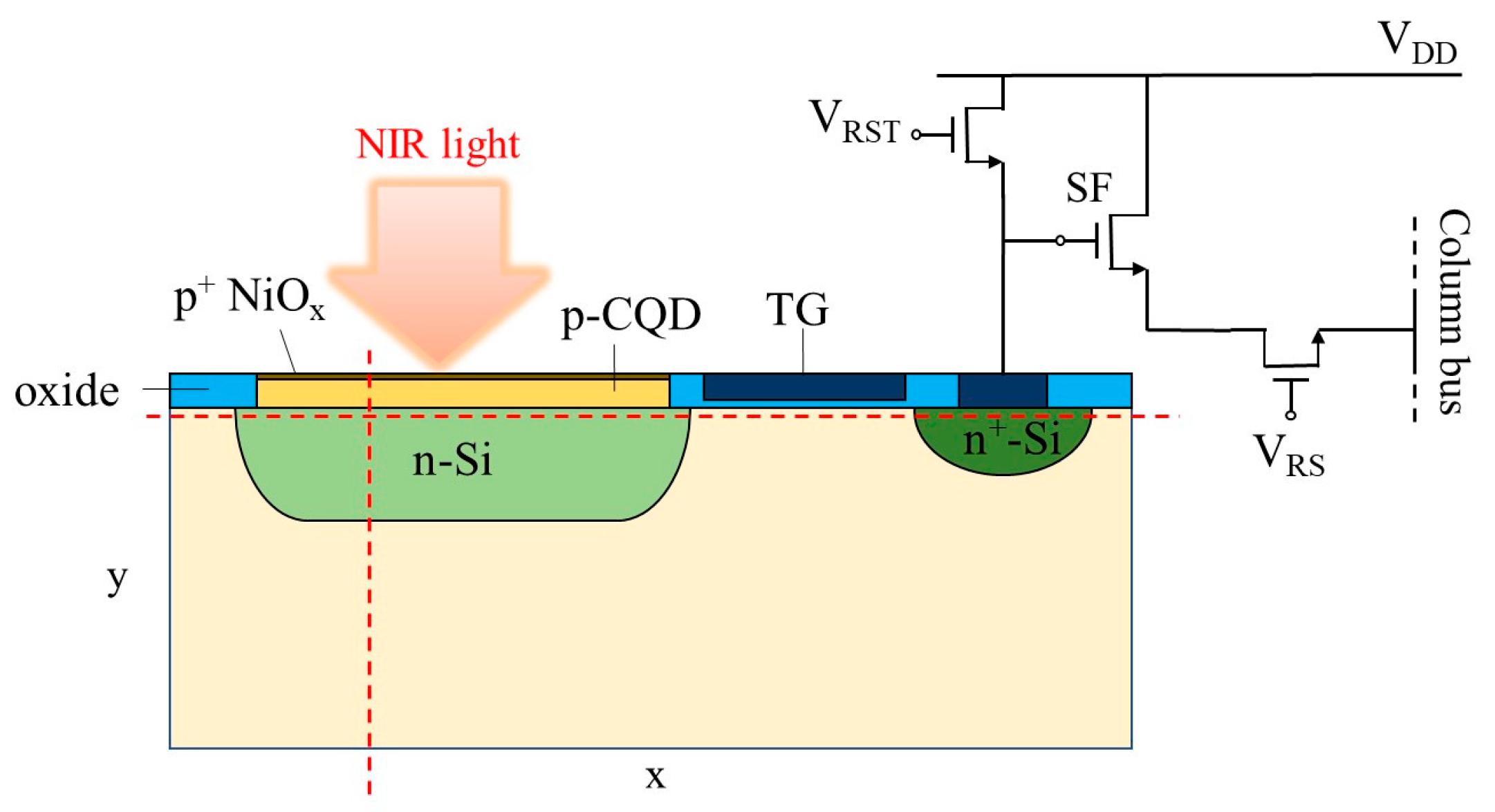
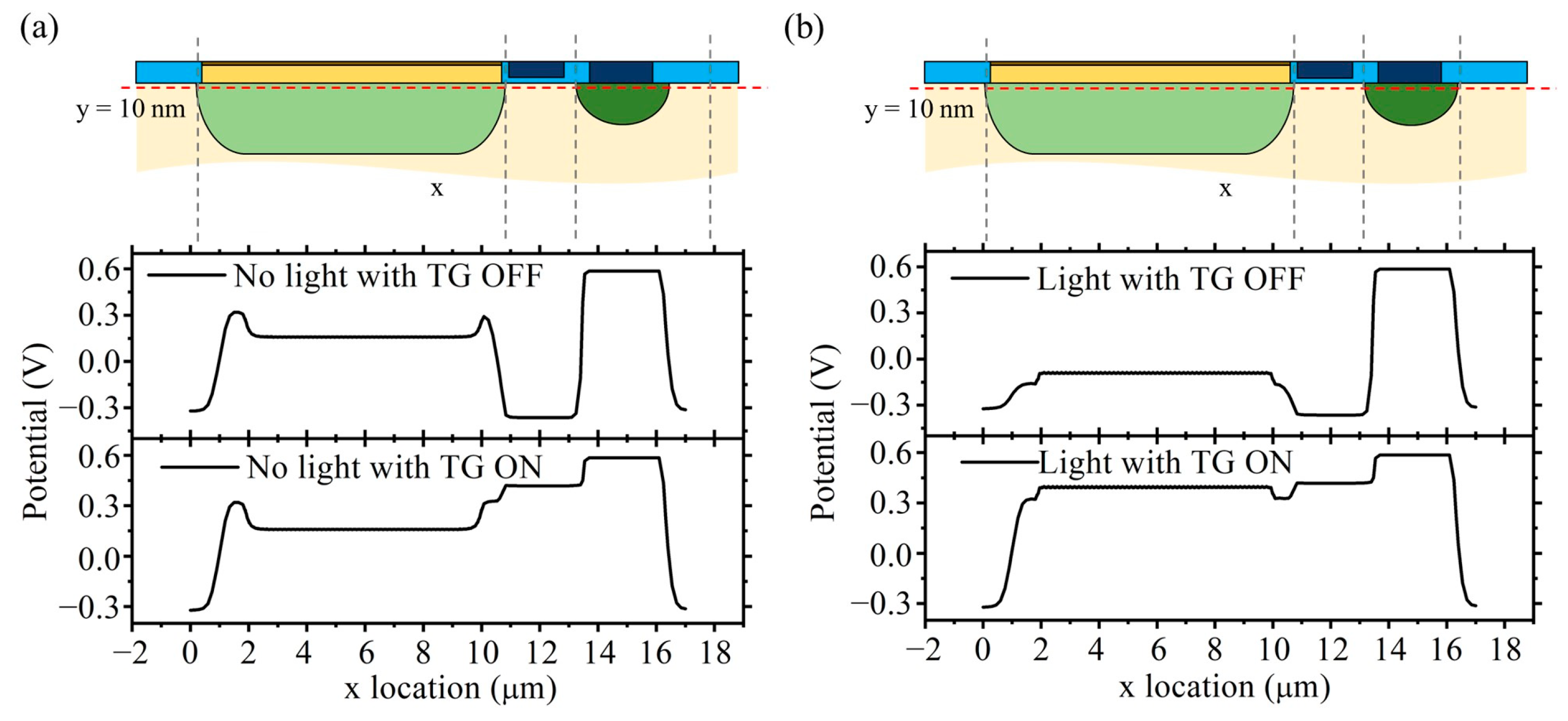
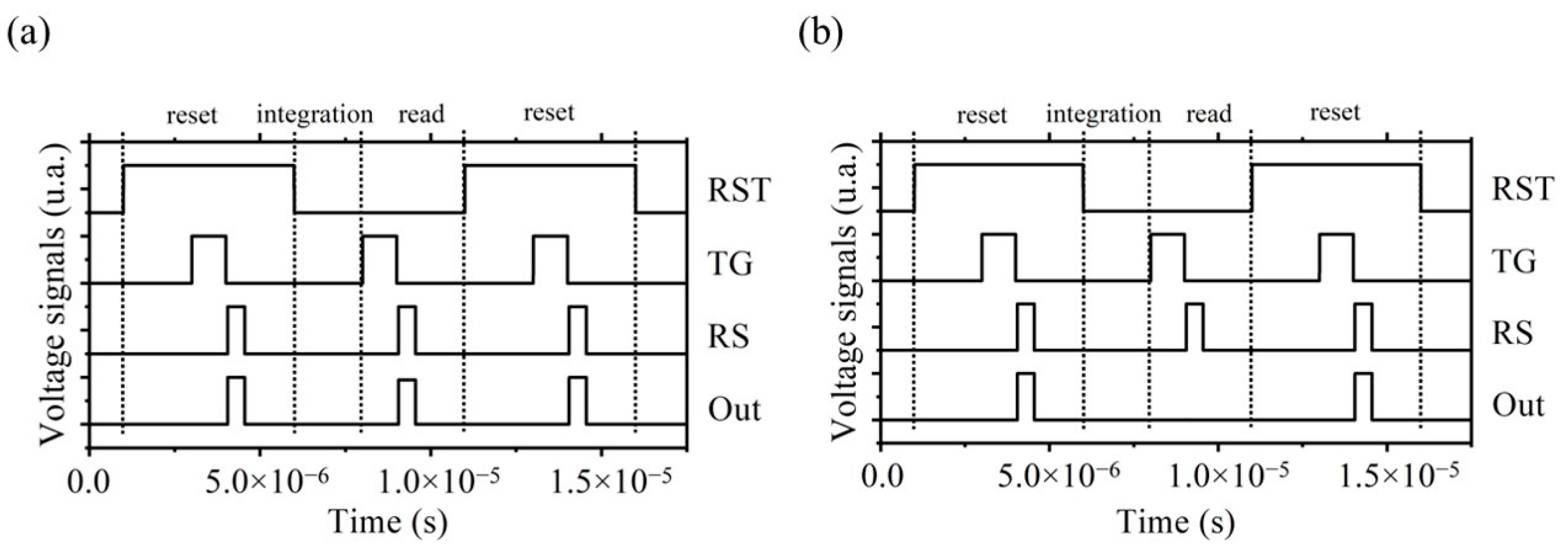
Abstract: The solution processibility of colloidal quantum dots (CQDs) promises a straightforward integration with Si readout integrated circuits (Si-ROICs), which enables a near-infrared (NIR) CMOS image sensor (CIS; CMOS stands for complementary metal-oxide semiconductor). Previously demonstrated CQD NIR CISs were achieved through integrating CQD photodiode or PhotoFET with Si-ROCIs. Here, we conduct a simulation study to investigate the feasibility of a NIR CIS enabled by another integration strategy, that is, by forming a CQD-Si heterojunction. Simulation results clearly show that each active pixel made of CQD-Si heterojunction photodiode on the CIS sensitively responds to NIR light, and generated photocarriers induce changes in electrostatic potentials in the active pixel. The potential changes are read out through the integrated circuits as validated by the readout timing sequence simulation.
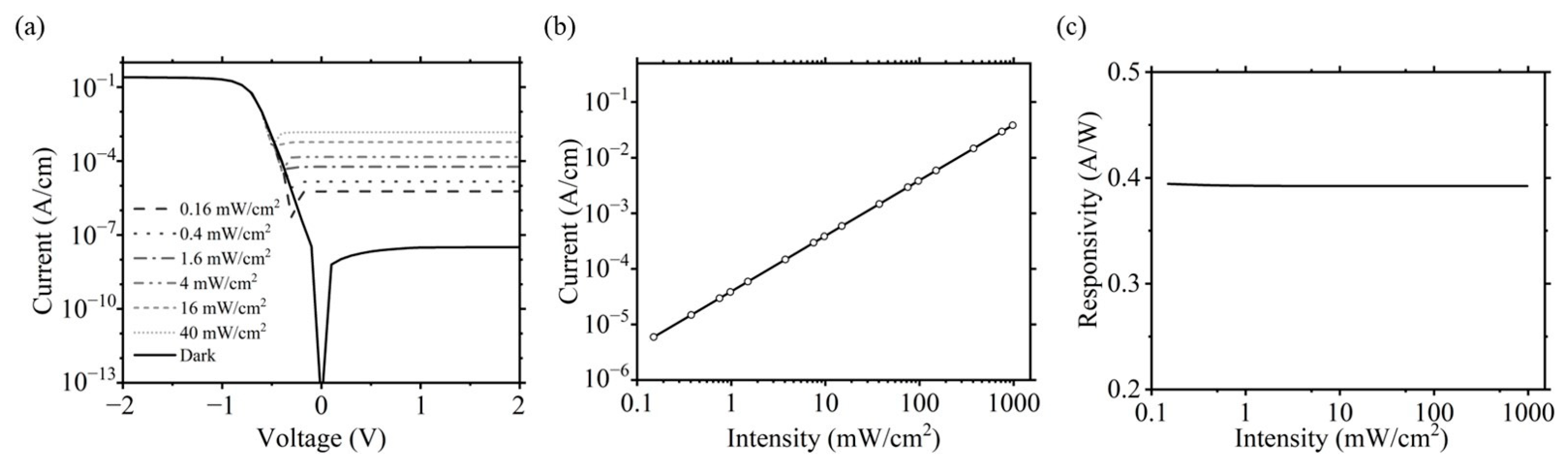
(a) I-V curves of NiO/CQD/Si heterojunction photodiode in the dark and various light intensities. (b) Photocurrent at various intensities. (c) Responsivity values as a function of intensity showing good linearity.
0 Response to "Paper on NIR quantum dot sensor"
Post a Comment